final关键字
final关键字代表最终、不可改变的
常见4种用法:
可以用来修饰一个类
可以用来修饰一个方法
还可以用来修饰一个局部变量
还可以用来修饰一个成员变量
用来修饰一个类
类1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package com.tipdm.Demo01;
public final class MyClass {
public void method(){
System.out.println("方法执行");
}
}
|
类2:
1
2
3
4
5
| package com.tipdm.Demo01;
public class MySubClass {
}
|
不能使用一个final类作为父类
用来修饰一个方法
当final关键字用来修饰一个方法的时候,这个方法就算最终方法,也就是不能被覆盖重写。
格式:
1
2
3
| 修饰符 final 返回值类型 方法名称(参数列表){
}
|
父类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| package com.tipdm.Demo02;
public class Fu {
public final void method(){
System.out.println("父类方法执行");
}
}
|
子类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package com.tipdm.Demo02;
public class Zi extends Fu{
}
|
注意事项:
- 对于类、方法来说,abstract关键字和final关键字不能同时使用,因为矛盾。
用来修饰局部变量
Student类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| package com.tipdm.Demo03;
public class Student {
private String name;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
|
主类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| package com.tipdm.Demo03;
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 10;
System.out.println(num1);
num1 = 20;
System.out.println(num1);
final int num2 = 200;
System.out.println(num2);
final int num3;
num3 = 30;
Student stu1 = new Student("赵丽颖");
System.out.println(stu1.getName());
System.out.println(stu1);
stu1 = new Student("霍建华");
System.out.println(stu1.getName());
System.out.println(stu1);
System.out.println("======================");
final Student stu2 = new Student("高圆圆");
System.out.println(stu2.getName());
System.out.println(stu2);
stu2.setName("赵又廷");
System.out.println(stu2.getName());
System.out.println(stu2);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| 10
20
200
赵丽颖
com.tipdm.Demo03.Student@1b6d3586
霍建华
com.tipdm.Demo03.Student@4554617c
======================
高圆圆
com.tipdm.Demo03.Student@74a14482
赵又廷
com.tipdm.Demo03.Student@74a14482
进程已结束,退出代码0
|
用来修饰成员变量
对于成员变量来说,如果使用final关键字修饰,那么这个变量也照样是不可改变.
由于成员变量具有默认值,所以用了final之后必须手动赋值,不会再给默认值了.
对于final的成员变量,要么使用直接赋值,要么通过构造方法赋值.二者选其一
必须保证类当中所有重载的构造方法,都最终会对final的成员变量进行赋值.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| package com.tipdm.Demo03;
public class Person {
private final String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person() {
name = "关晓彤";
}
}
|
Java种四种权限修饰符
Java中有四种权限修饰符:
public > protected > (default) > private
|
Public |
protcted |
(default) |
private |
| 同一个类(我自己) |
YES |
YES |
YES |
YES |
| 同一个包(我邻居) |
YES |
YES |
YES |
NO |
| 不同包子类(我儿子) |
YES |
YES |
NO |
NO |
| 不同包非子类(陌生人) |
YES |
NO |
NO |
NO |
注意事项:(default)并不是关键字”default”,而是根本不写。
文件结构:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| Demo04
├─demo1.java
├─MyAnother.java
├─MyClass.java
└─sub
├─MySon.java
└─Other.java
|
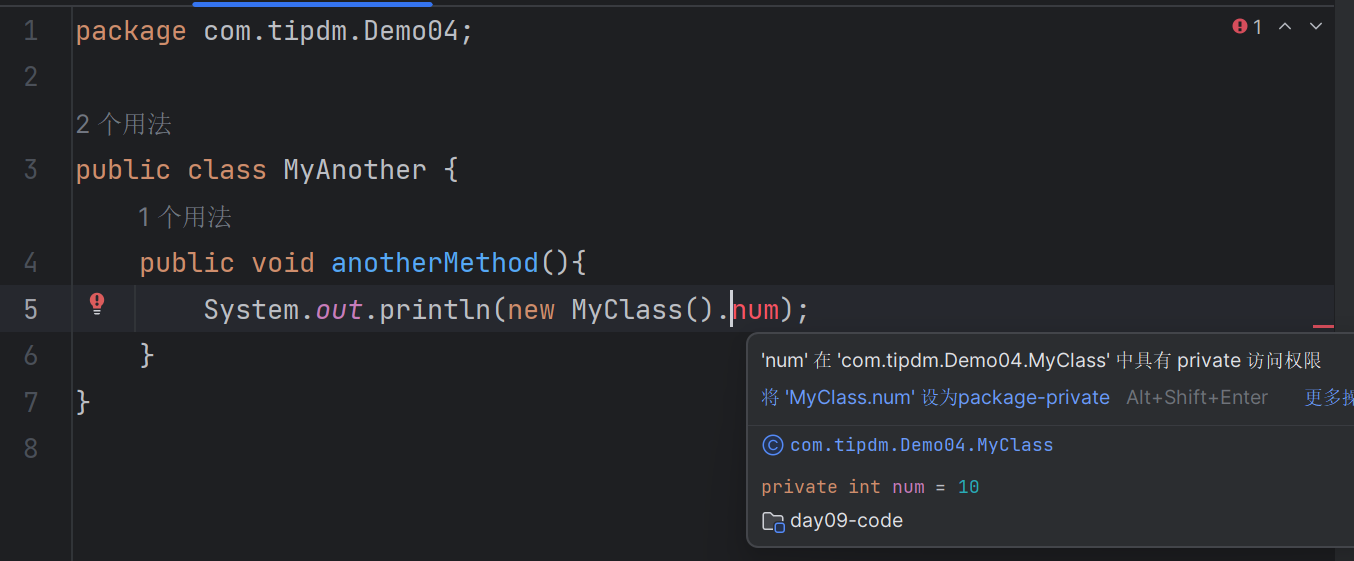
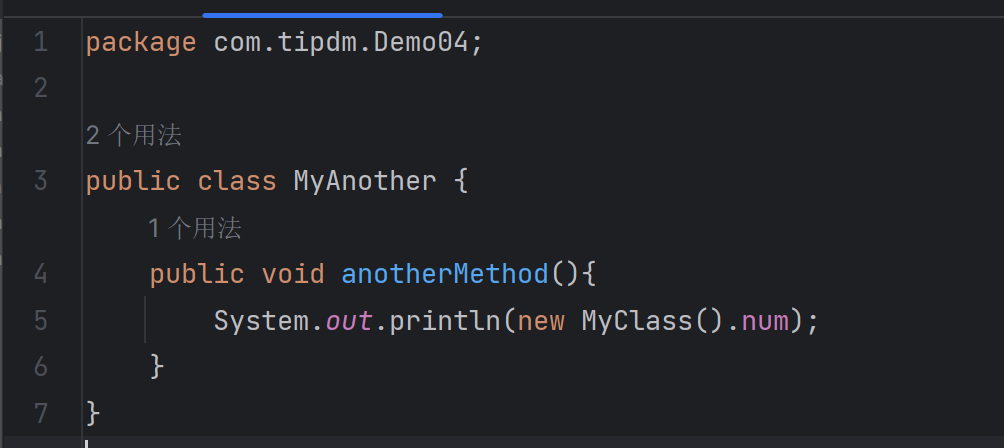
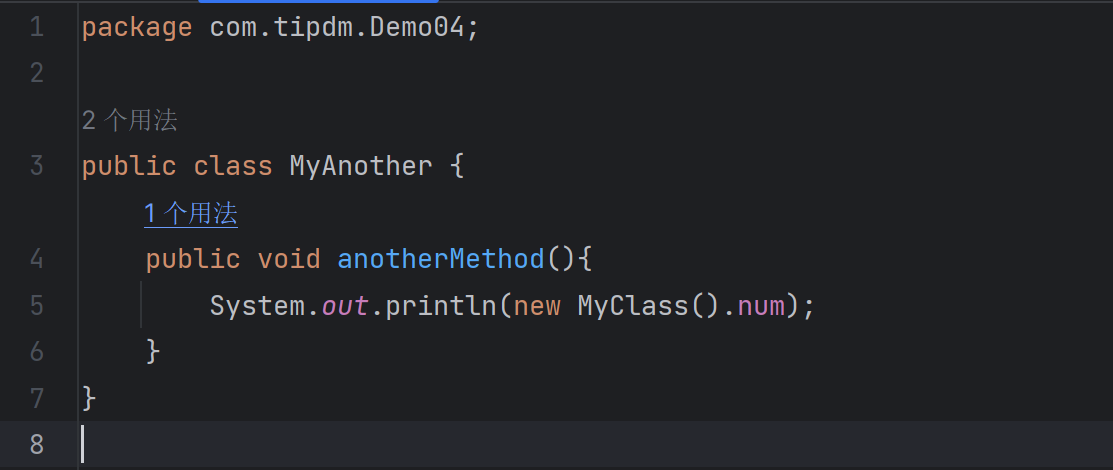
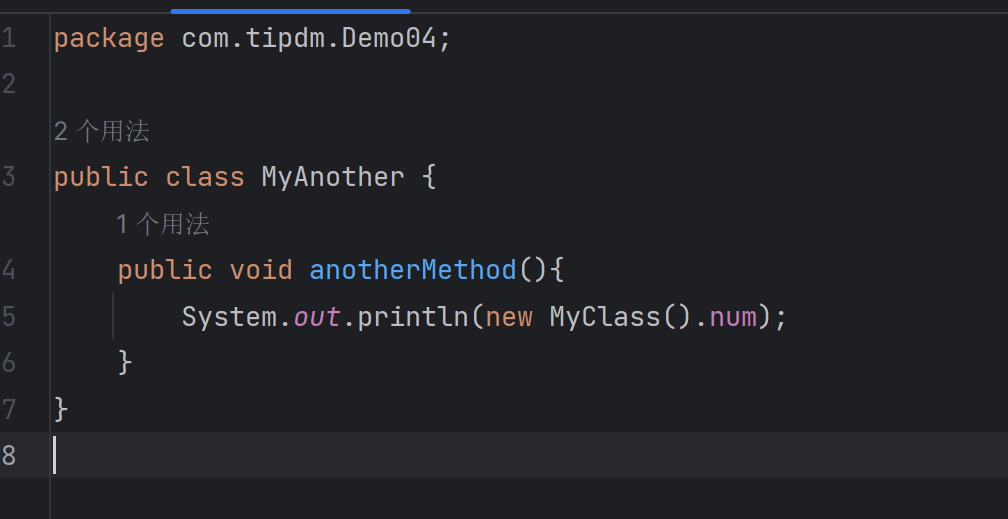
MyAnother类(位于同一个包):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| package com.tipdm.Demo04;
public class MyAnother {
public void anotherMethod(){
}
}
|
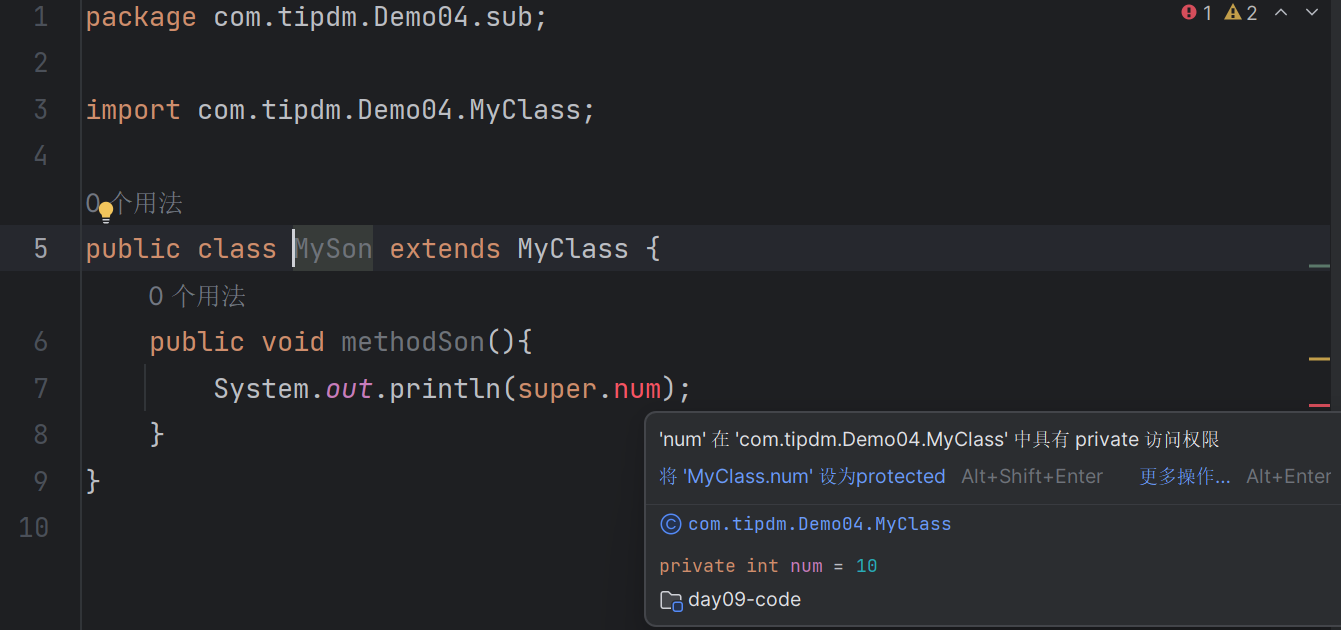
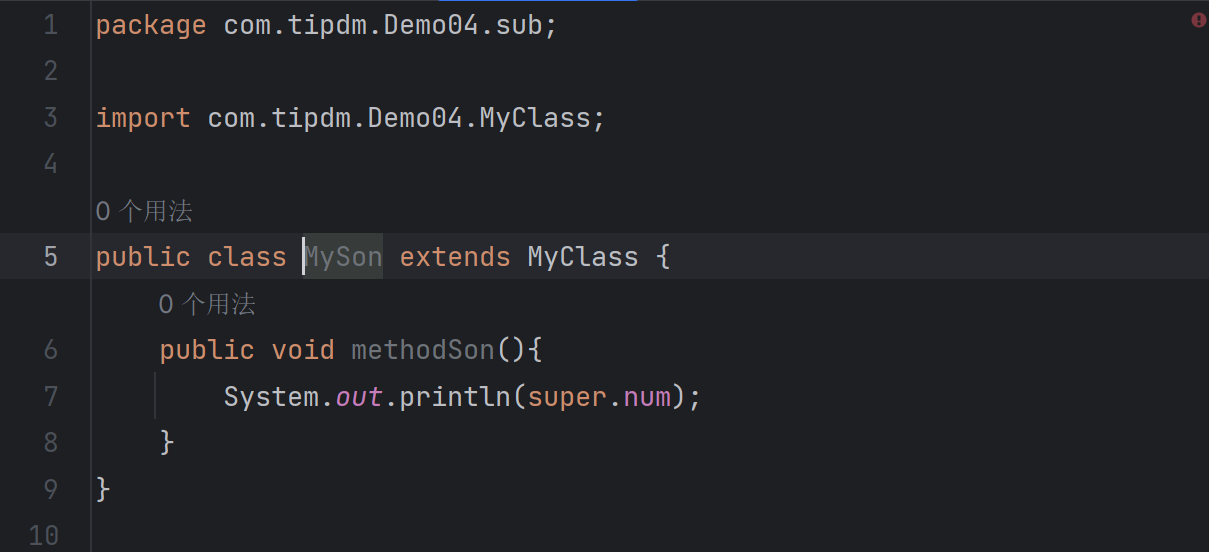
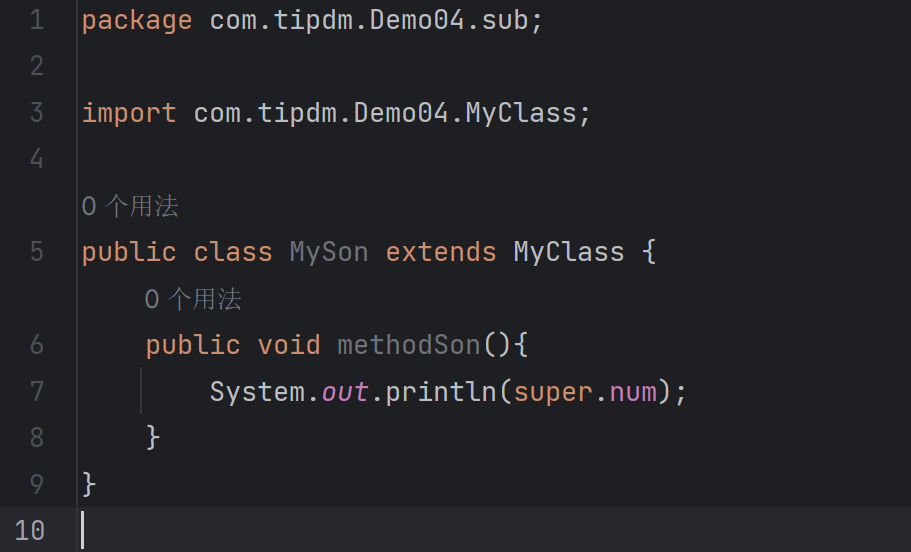
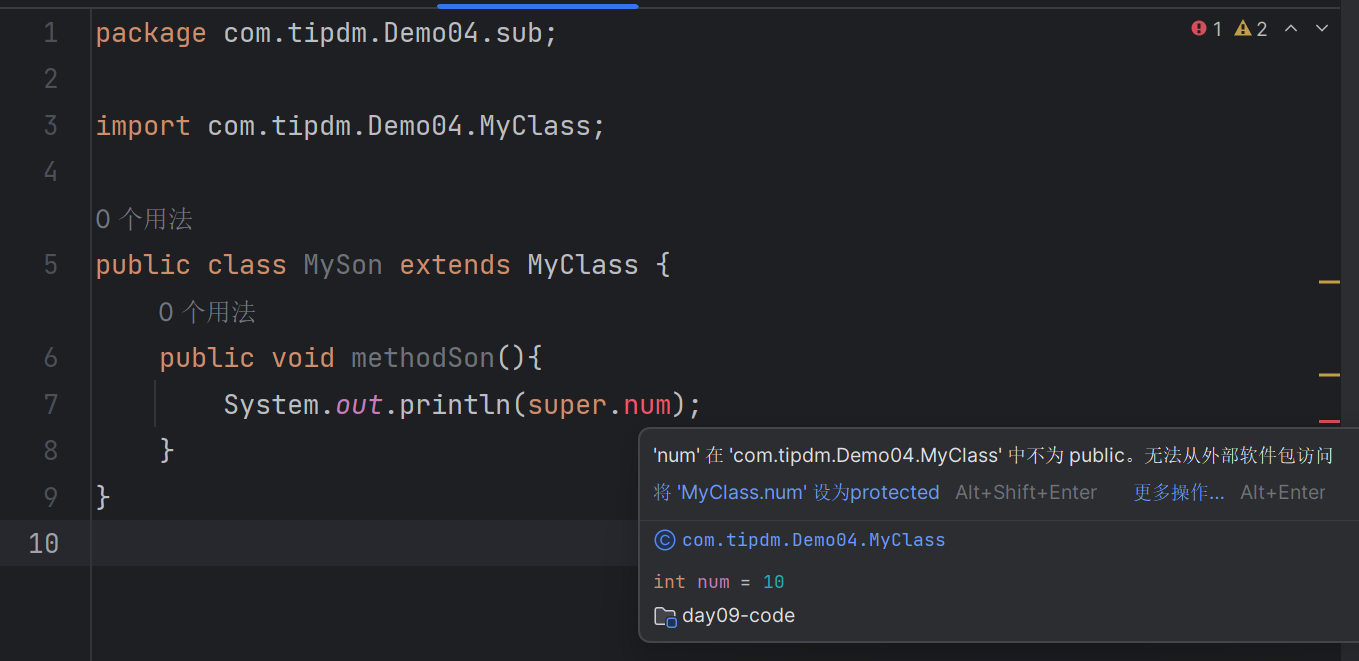
sub\MySon类(位于不同包子类):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package com.tipdm.Demo04.sub;
import com.tipdm.Demo04.MyClass;
public class MySon extends MyClass {
public void methodSon(){
}
}
|
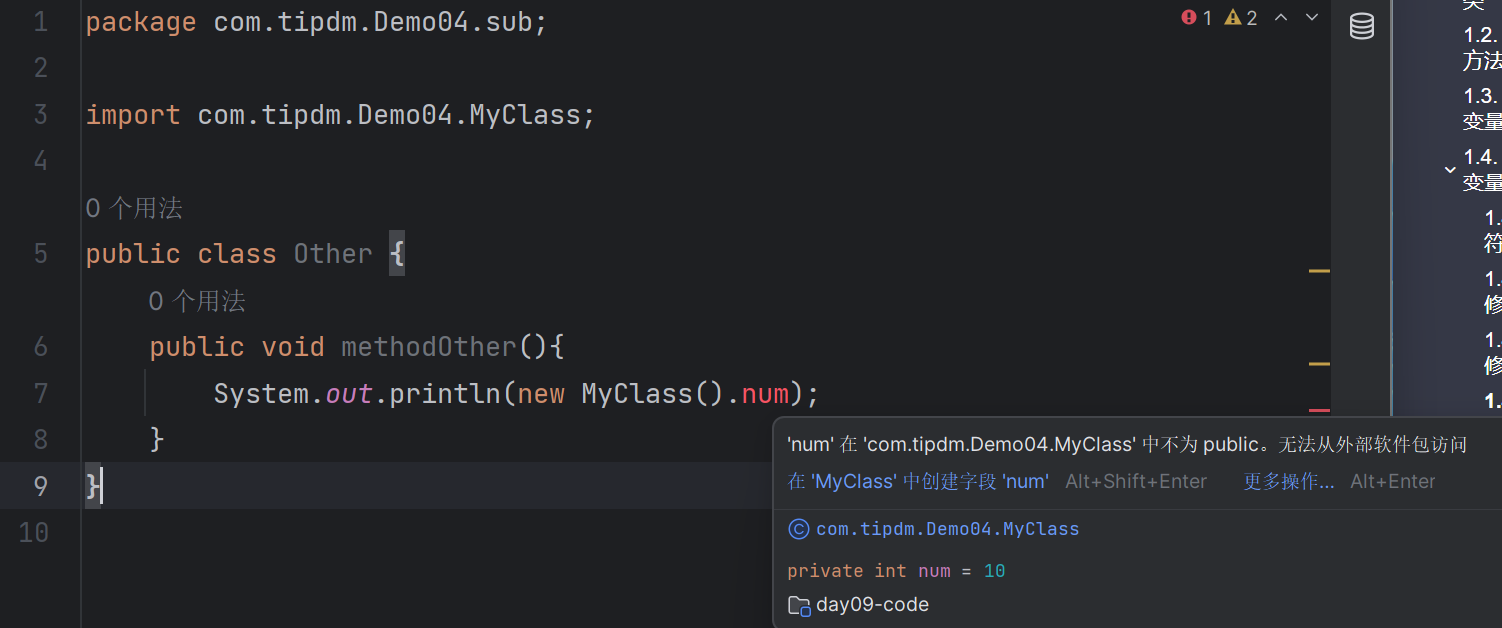
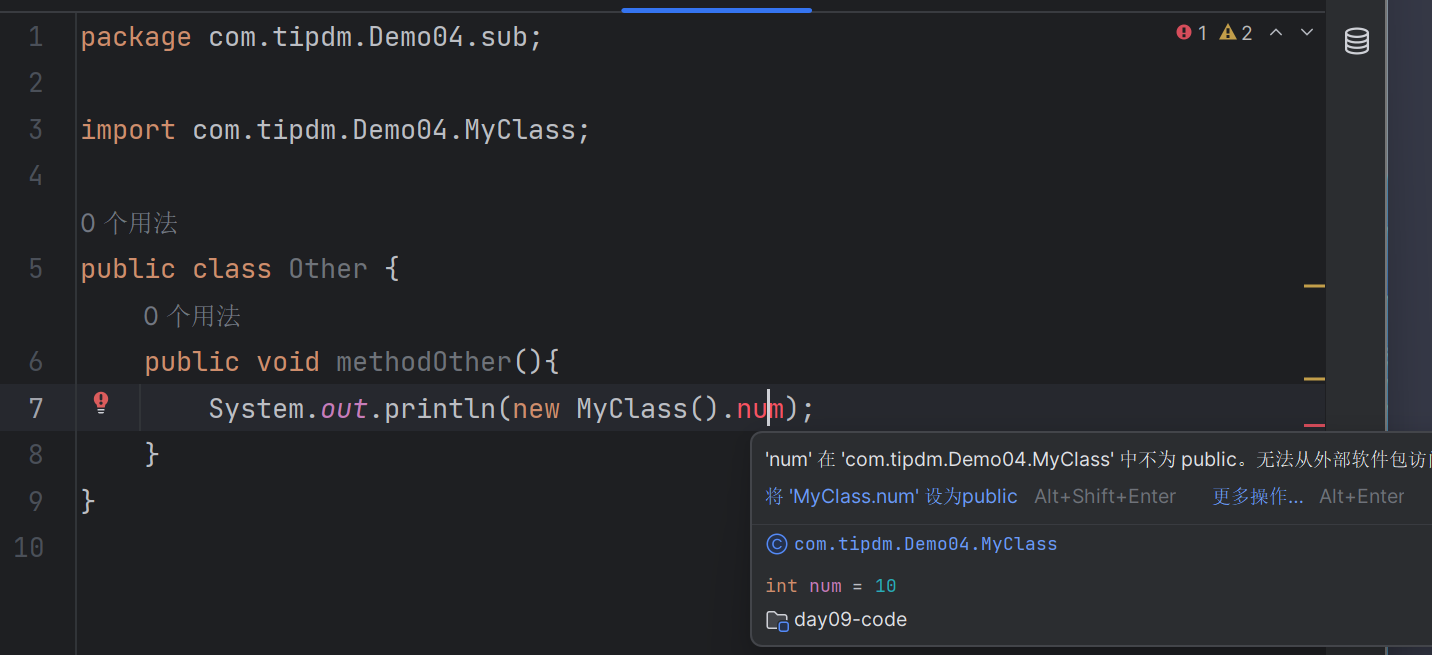
sub\Other类(不同包非子类):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package com.tipdm.Demo04.sub;
import com.tipdm.Demo04.MyClass;
public class Other {
public void methodOther(){
System.out.println(new MyClass().num);
}
}
|
在此,我们让不同的包全部去请求MyClass中的num成员变量,后续想num变量赋予不同的权限修饰符,查看其他把的引用状态是否发生变化。
public修饰符
MyClass类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package com.tipdm.Demo04;
public class MyClass {
public int num = 10;
public void method(){
System.out.println(num);
}
}
|
这个时候可以看到其他各个包的请求都是正常的。

protected修饰符
MyClass类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package com.tipdm.Demo04;
public class MyClass {
protected int num = 10;
public void method(){
System.out.println(num);
}
}
|
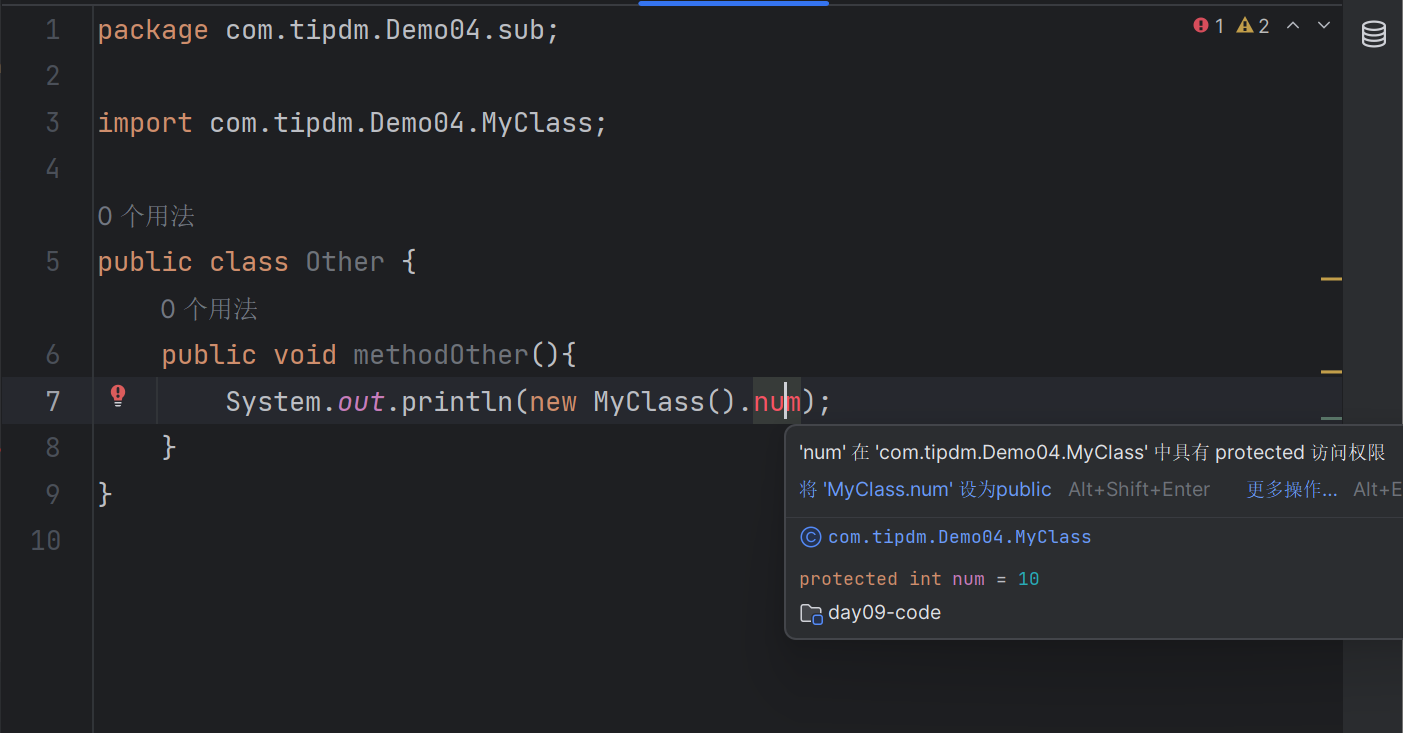
(default)修饰符
MyClass类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package com.tipdm.Demo04;
public class MyClass {
int num = 10;
public void method(){
System.out.println(num);
}
}
|
private修饰符
MyClass类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| package com.tipdm.Demo04;
public class MyClass {
private int num = 10;
public void method(){
System.out.println(num);
}
}
|