OutputFormat是MapReduce输出的基类,所有实现MapReduce输出都实现了OutputFormat接口。
在MR中默认的使用的OutputFormat子类是TextOutputFormat。
源码分析
打开IDEA,双击两下Shift键搜索OutputFormat查看源码,然后将光标防放在OutputFormat类名上按Ctrl + H查看层次结构。
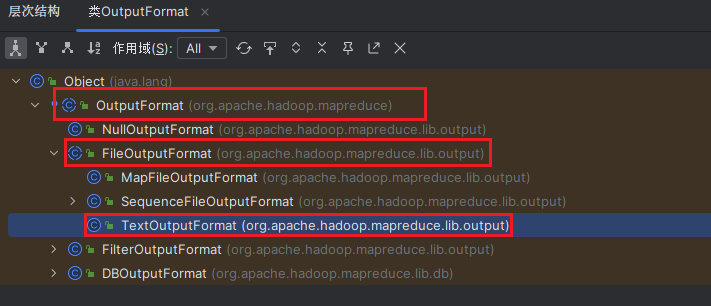
- 首先点击
OuputFormat查看源码,该类是一个抽象类,有3个抽象方法。
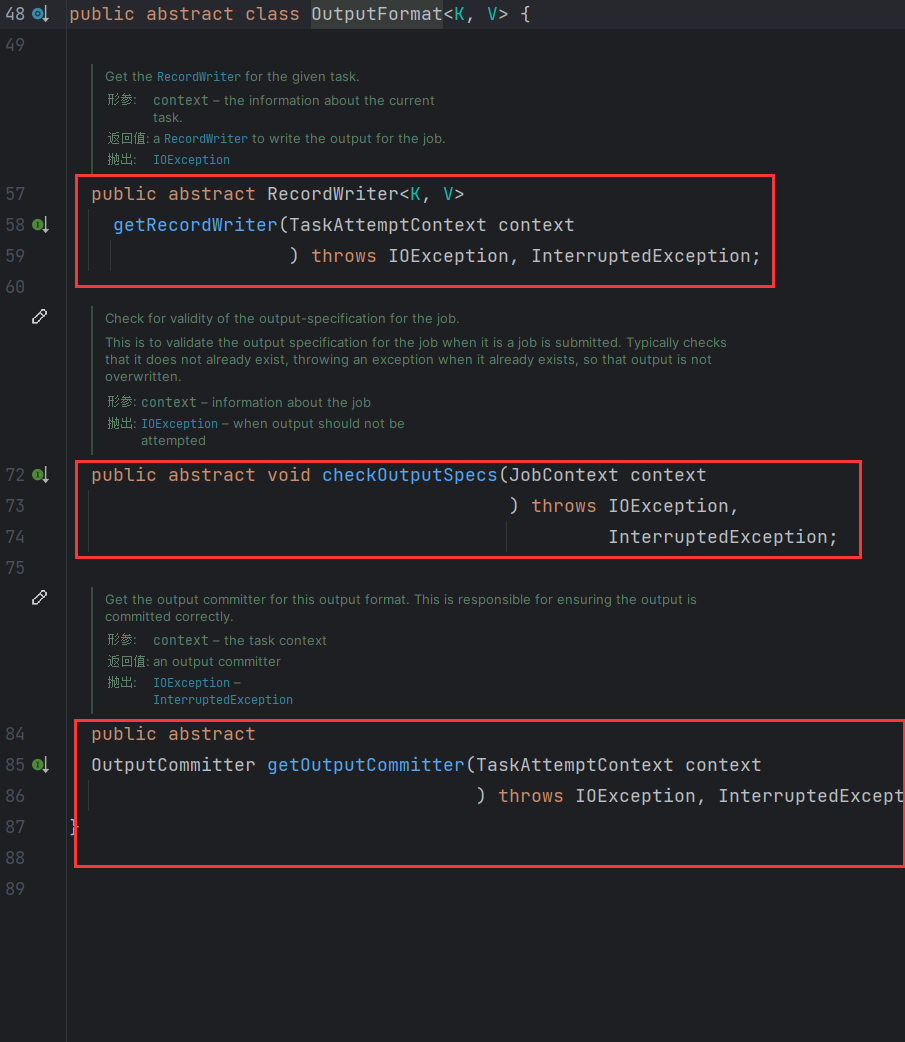
RecordWriter:负责写出数据。checkOutputSpecs:负责检查输出路径。getOutputCommitter:获取输出提交对象。
- 然后再点击
FileOutputFormat查看源码,该方法继承自OutputFormat也是一个抽象方法。
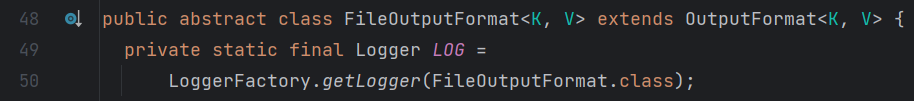
在该方法中重写了checkOutputSpecs和getOutputCommitter这两个方法。
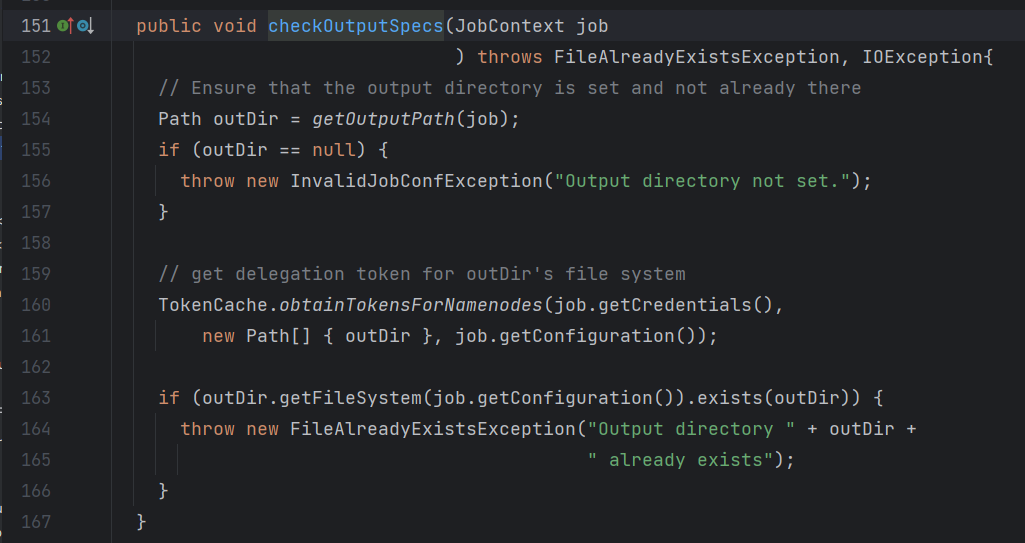
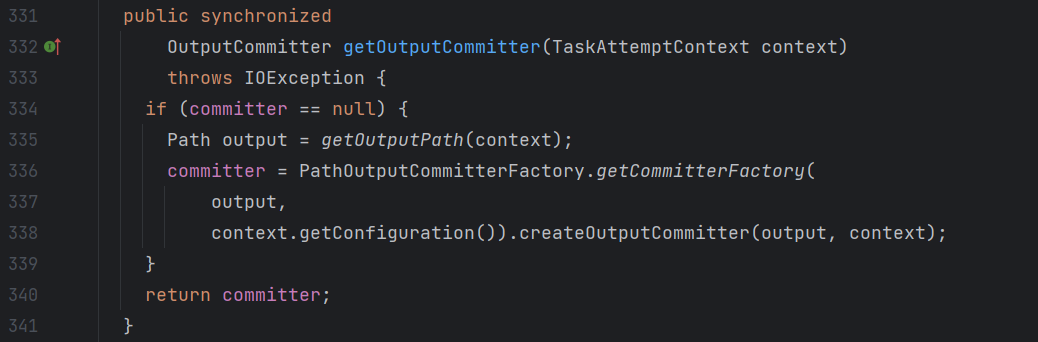
- 接下来继续点击
TextOutputFormat,查看源码。

该类继承自FileOutputFormat并重写了RecodWriter方法。也是默认的OutputFormat的实现类。
案例实战
案例目标:对日志文件进行统计,把包含tipdm的网址放入一个文件,其他网址放入另一个文件。
文件内容如下所示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| http://www.baidu.com
http://www.google.com
http://cn.bing.com
http://www.tipdm.com
http://www.sohu.com
http://www.sina.com
http://www.sin2a.com
http://www.sin2desa.com
http://www.sindsafa.com
http://cn.bing.com
http://www.tipdm.com
http://www.sohu.com
http://www.sina.com
http://www.sin2a.com
http://cn.bing.com
http://www.tipdm.com
http://www.sohu.com
http://www.sina.com
http://www.sin2a.com
http://cn.bing.com
http://www.tipdm.com
http://www.sohu.com
http://www.sina.com
http://www.sin2a.com
http://cn.bing.com
http://www.tipdm.com
http://www.sohu.com
http://www.sina.com
http://www.sin2a.com
|
默认输出格式
按照前面已经讲过的内容,无非做的就是一个自定义分区。比较简单,直接给出源码如下所示。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| package com.tipdm.mr.outputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class LogMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(value, NullWritable.get());
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| package com.tipdm.mr.outputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class LogReducer extends Reducer<Text, NullWritable, Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Reducer<Text, NullWritable, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (NullWritable value : values) {
context.write(key, NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| package com.tipdm.mr.outputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
public class LogPartition extends Partitioner<Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
public int getPartition(Text text, NullWritable nullWritable, int numPartitions) {
String string = text.toString();
if (string.contains("tipdm")){
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| package com.tipdm.mr.outputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class LogDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setNumReduceTasks(2);
job.setPartitionerClass(LogPartition.class);
job.setJarByClass(LogDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(LogMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(LogReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("..\\ioText\\input4"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("..\\ioText\\output"));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
|
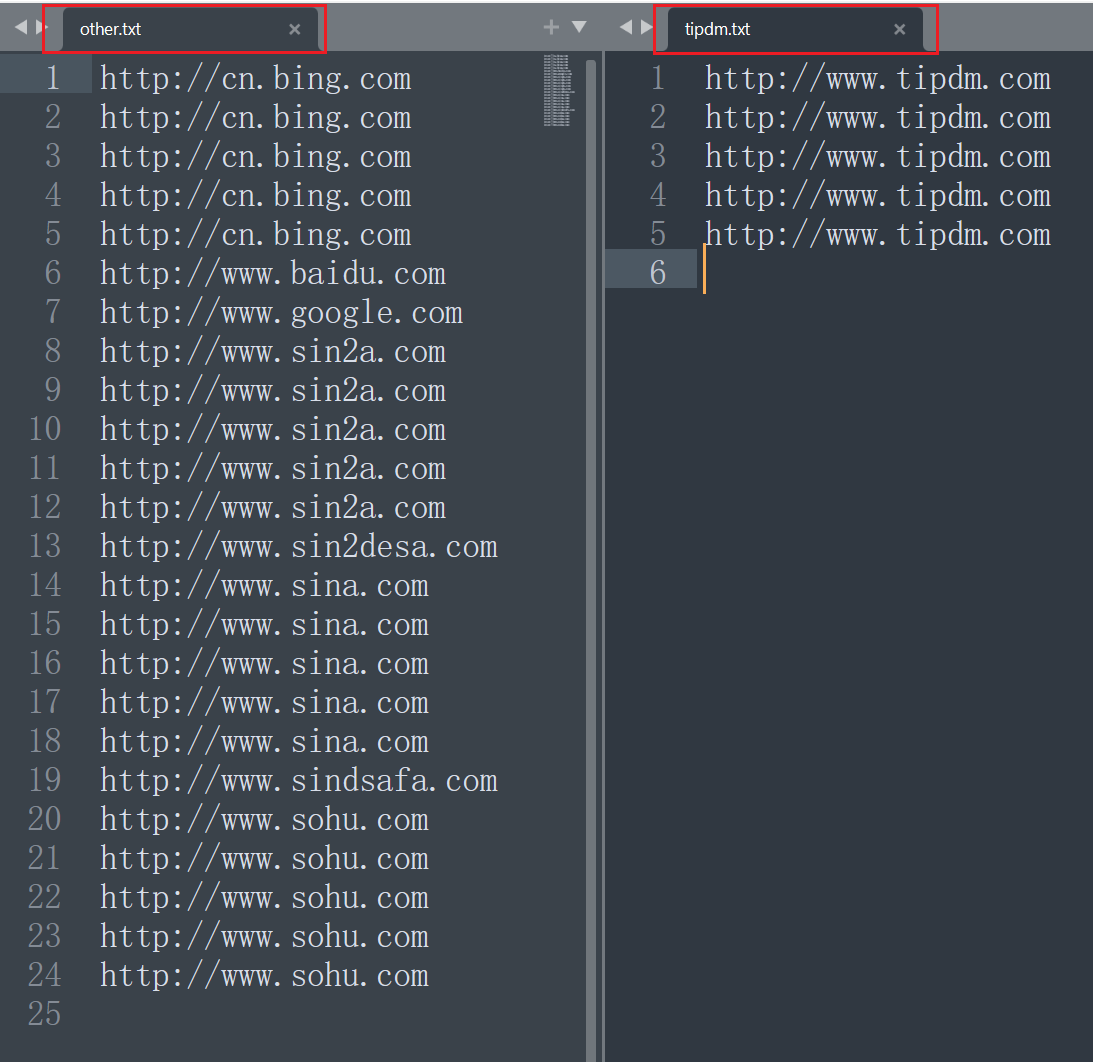
结果展示:
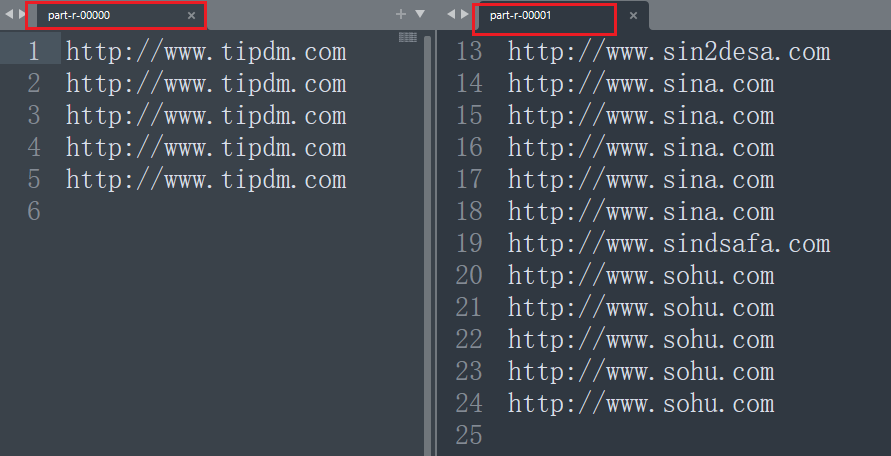
上述结果虽然能够满足要求,但是有一个问题是每次获取到的输出文件命名规则都是一样的part-r-0xxx。
如果现在还是按照上面的规则生成文件,但是要求生成的文件为tipdm.txt和other.txt这两个文件,这个时候默认是输出格式就无法满足了。要想满足这个需求,这个时候就需要使用到自定义的OutputFormat。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| package com.tipdm.mr.outputformat2;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyFileOutputFormat extends FileOutputFormat<Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
public RecordWriter<Text, NullWritable> getRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext job) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return new MyRecordWriter(job);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| package com.tipdm.mr.outputformat2;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataOutputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyRecordWriter extends RecordWriter<Text, NullWritable> {
private FSDataOutputStream tipdm_fos;
private FSDataOutputStream other_fos;
public MyRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext job) throws IOException {
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(job.getConfiguration());
Path outputPath = FileOutputFormat.getOutputPath(job);
tipdm_fos = fs.create(new Path(outputPath, "tipdm.txt"));
other_fos = fs.create(new Path(outputPath, "other.txt"));
}
@Override
public void write(Text key, NullWritable value) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String string = key.toString() + '\n';
if (string.contains("tipdm")){
tipdm_fos.write(string.getBytes());
}else{
other_fos.write(string.getBytes());
}
}
@Override
public void close(TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
tipdm_fos.close();
other_fos.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| package com.tipdm.mr.outputformat2;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class LogMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(value, NullWritable.get());
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| package com.tipdm.mr.outputformat2;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class LogReducer extends Reducer<Text, NullWritable, Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Reducer<Text, NullWritable, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (NullWritable value : values) {
context.write(key, NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| package com.tipdm.mr.outputformat2;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class LogDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setOutputFormatClass(MyFileOutputFormat.class);
job.setJarByClass(LogDriver.class);
job.setMapperClass(LogMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(LogReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("..\\ioText\\input4"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("..\\ioText\\output"));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
|
结果如图所示:
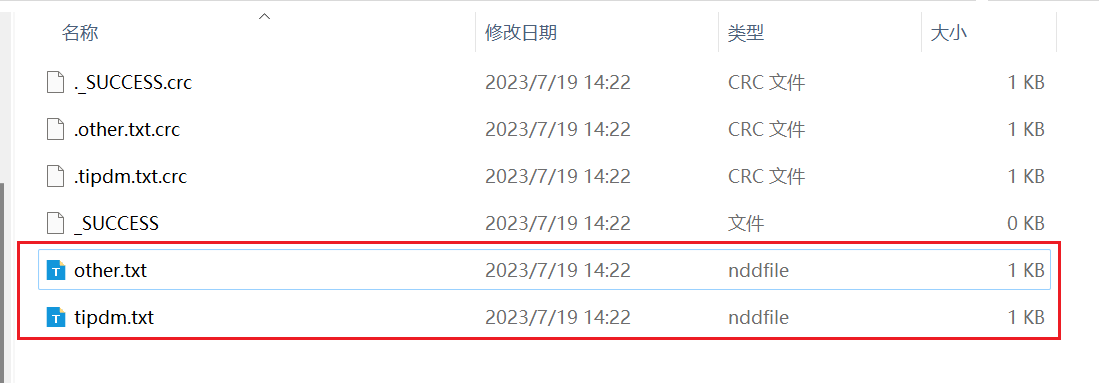
Join应用
MapJoin
概述
Map Join适用于一张表十分小、一张表很大的场景。
问题引出:在Reduce端处理过多的表,非常容易产生数据倾斜。怎么办?
对于集群系统,一般缓存是分布式的,即不同节点负责一定范围的缓存数据。我们把缓存数据分散度不够,导致大量的缓存数据集中到了一台或者几台服务节点上,称为数据倾斜。一般来说数据倾斜是由于负载均衡实施的效果不好引起的。
处理方式:在Map端缓存多张表,提前处理业务逻辑,这样增加Map端业务,减少Reduce端数据的压力,尽可能的减少数据倾斜。
案例实操
需求:
有两个文件,输入如下所示。
| id |
pid |
amount |
| 1001 |
01 |
1 |
| 1002 |
02 |
2 |
| 1003 |
03 |
3 |
| 1004 |
01 |
4 |
| 1005 |
02 |
5 |
| 1006 |
03 |
6 |
| pid |
pname |
| 01 |
小米 |
| 02 |
华为 |
| 03 |
格力 |
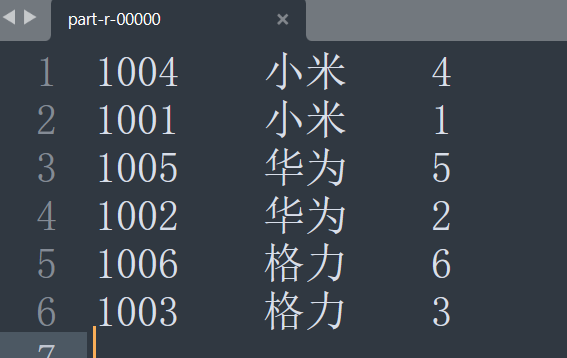
现在需要做一个对应,将order.txt中的pid对应到pd.txt中具体的pname。
| id |
pname |
amount |
| 1001 |
小米 |
1 |
| 1004 |
小米 |
4 |
| 1002 |
华为 |
2 |
| 1005 |
华为 |
5 |
| 1003 |
格力 |
3 |
| 1006 |
格力 |
6 |
这个时候采用的方式是在Map阶段中完成该任务,提前把较小的表提前缓存到Map阶段之前。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
| package com.tipdm.mr.mapJoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MJMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> {
private Map map = new HashMap();
private Text outKey = new Text();
@Override
protected void setup(Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
FileSystem fs = null;
FSDataInputStream fis = null;
BufferedReader bufferedReader = null;
try{
fs = FileSystem.get(context.getConfiguration());
URI[] cacheFiles = context.getCacheFiles();
URI uri = cacheFiles[0];
fis = fs.open(new Path(uri));
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8"));
String linedata = "";
while ((linedata = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
String[] split = linedata.split("\t");
map.put(split[0], split[1]);
}
}finally {
if (fs != null){
fs.close();
}
if (fis != null){
fis.close();
}
if (bufferedReader != null){
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
}
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String string = value.toString();
String[] split = string.split("\t");
outKey.set(split[0] + "\t" + map.get(split[1]) + "\t" + split[2]);
context.write(outKey, NullWritable.get());
}
@Override
protected void cleanup(Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
super.cleanup(context);
}
}
|
在Mapper阶段有两个方法可以重写,用来达到我们的一些需求:
setup:该方法是在map方法之前执行一次。可以在该方法中提前缓存在map方法中要使用到的一些数据。由于map方法在整个MR任务中会重复调用,把io操作放到map方法中执行肯定是不合适的,会造成大量的计算资源浪费。cleanup:该方法是在map方法完后之后执行一次。这里可以配合setup方法使用,如果在setup中开启的文件资源在map阶段中要使用,那么在setup中就不能关闭该资源,这个时候就可以在cleanup中运行释放资源的代码,防止资源被占用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| package com.tipdm.mr.mapJoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
public class MJDriver{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, URISyntaxException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration());
job.addCacheFile(new URI("file:///E:/学习笔记/大数据开发笔记/5_Hadoop/ioText/input5/pd.txt"));
job.setNumReduceTasks(0);
job.setMapperClass(MJMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("E:\\学习笔记\\大数据开发笔记\\5_Hadoop\\ioText\\input5\\order.txt"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("E:\\学习笔记\\大数据开发笔记\\5_Hadoop\\ioText\\output"));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
|
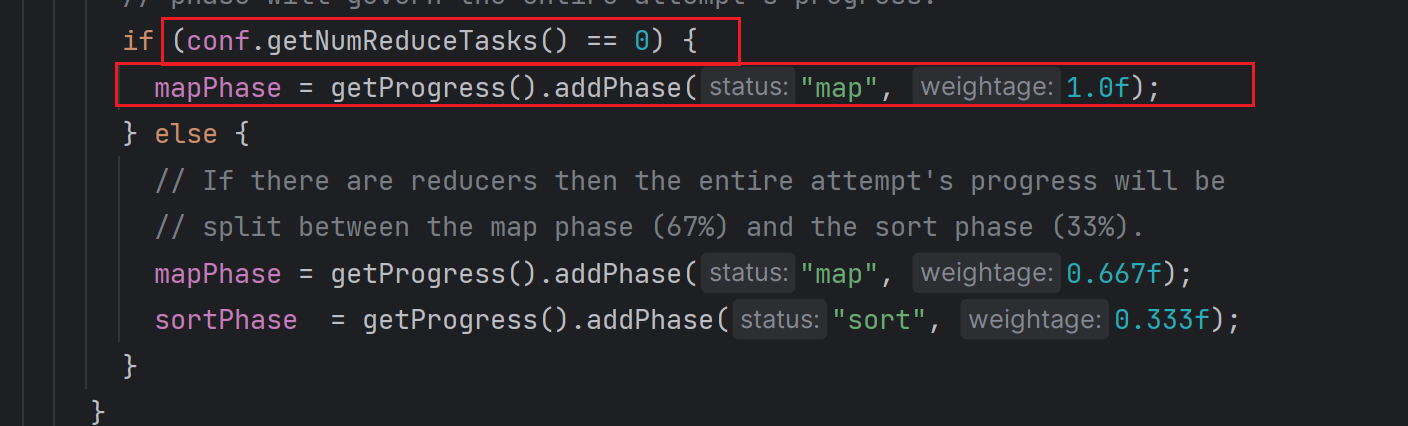
此时不需要Reduce阶段,所以可以不写Reducer类。
并且为了加快运算效率,可以在Driver中设置ReduceTask的数量为0,这样就不会执行排序操作。
在MapTask的源码中也可以看到,如下所示:
并且为了在Map阶段中读取缓存文件,需要提前知道缓存文件的路径或者是URI。在job对象中有方法可以达到我们的想要的这个效果addCacheFile方法。
1
| public void addCacheFile(URI uri)
|
在addcacheFile方法中需要传入的参数为URI对象。
URI的写法:
Windows:file:///D:/io/cache/a.txtHDFS:hdfs://cache/a.txt
运行效果:
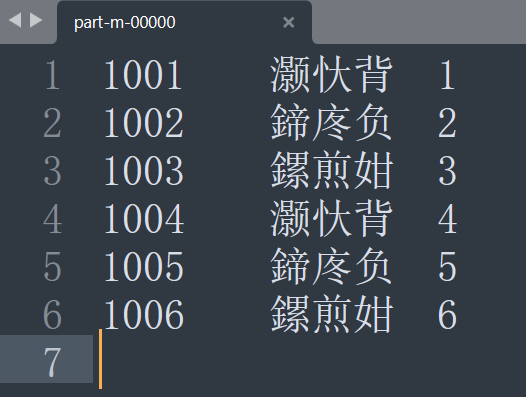
可以看到此时出现了乱码。这个时候需要在创建BufferedReader时设置编码为UTF-8。

再次运行查看效果(注意:需要先将output文件删除):
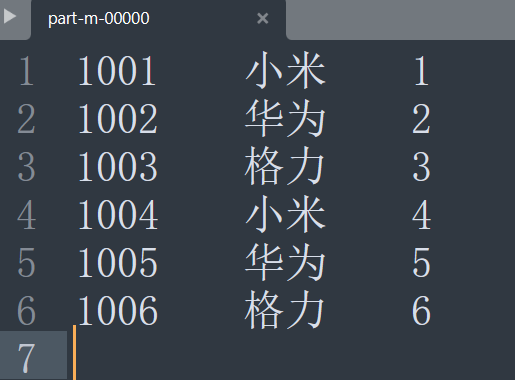
结果正常。
ReduceJoin
还是上述这个案例,在Reduce阶段进行连接该如何操作。
思路如下:
将两个表同时读取进来
然后首先对pid进行排序,然后当pid相同时再按照pname进行排序。
然后按照pid进行分组。
注意:这里分组需要自定义分组,默认情况下会按照排序的结果进行分组,不能满足我们的需求,所以需要自定义分组结果。
这样在Reduce阶段拿到的就是不同的pid为一组,由于前面对pname也进行了排序所以,现在拿到的分组结果,每一组的第一条数据是pd.txt中的内容,包含具体的pname,在后续对同组的其他数据直接赋值该pname即可。
为了满足上述需求,首先我们需要定义一个OrderBean类同时拥有id、pid、amount和pname。并且由于该OrderBean类需要放入到MR中进行计算和传输,所以需要可序列化并且还要后续对其按照某种规则进行排序。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
| package com.tipdm.mr.reduceJoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
public class OrderBean implements WritableComparable<OrderBean> {
private int id;
private int pid;
private int amount;
private String pname;
public OrderBean() {
}
public OrderBean(int id, int pid, int amount, String pname) {
this.id = id;
this.pid = pid;
this.amount = amount;
this.pname = pname;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getPid() {
return pid;
}
public void setPid(int pid) {
this.pid = pid;
}
public int getAmount() {
return amount;
}
public void setAmount(int amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
public String getPname() {
return pname;
}
public void setPname(String pname) {
this.pname = pname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return id + "\t" + pname + "\t" + amount;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(OrderBean o) {
if (this.pid == o.pid){
return -this.pname.compareTo(o.pname);
}
return this.pid - o.pid;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeInt(id);
out.writeInt(pid);
out.writeInt(amount);
out.writeUTF(pname);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
id = in.readInt();
pid = in.readInt();
amount = in.readInt();
pname = in.readUTF();
}
}
|
同时将两个文件读取进来,并按照不同的文件内容处理读取的数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| package com.tipdm.mr.reduceJoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import java.io.IOException;
public class RJMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderBean, NullWritable> {
private OrderBean outKey = new OrderBean();
private String filename;
@Override
protected void setup(Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderBean, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
filename = inputSplit.getPath().getName();
}
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderBean, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String string = value.toString();
String[] splits = string.split("\t");
if (filename.equals("order.txt")){
outKey.setId(Integer.parseInt(splits[0]));
outKey.setPid(Integer.parseInt(splits[1]));
outKey.setAmount(Integer.parseInt(splits[2]));
outKey.setPname("");
}else if(filename.equals("pd.txt")){
outKey.setPid(Integer.parseInt(splits[0]));
outKey.setPname(splits[1]);
}
context.write(outKey, NullWritable.get());
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| package com.tipdm.mr.reduceJoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class RJReducer extends Reducer<OrderBean, NullWritable, OrderBean, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(OrderBean key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Reducer<OrderBean, NullWritable, OrderBean, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Iterator<NullWritable> iterator = values.iterator();
iterator.next();
String first_pname = key.getPname();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
iterator.next();
key.setPname(first_pname);
context.write(key, NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
|
- 自定义分组
MyGroupingComparatorClass
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| package com.tipdm.mr.reduceJoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
public class MyGroupingComparatorClass extends WritableComparator {
public MyGroupingComparatorClass(){
super(OrderBean.class, true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
OrderBean o1 = (OrderBean) a;
OrderBean o2 = (OrderBean) b;
return o1.getPid() - o2.getPid();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| package com.tipdm.mr.reduceJoin;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class RJDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration());
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(MyGroupingComparatorClass.class);
job.setMapperClass(RJMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(RJReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(OrderBean.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(OrderBean.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("E:\\学习笔记\\大数据开发笔记\\5_Hadoop\\ioText\\input5"));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("E:\\学习笔记\\大数据开发笔记\\5_Hadoop\\ioText\\output5"));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
|
MR开发总结
- 默认使用的实现类是:
TextInputFormat
TextInputFormat的功能逻辑是:一次读一行文本,然后将该行的起始偏移量作为key,行内容作为value返回。CombineTextInputFormat可以把多个小文件合并成一个切片处理,提高处理效率。
逻辑处理接口:Mapper
用户根据业务需求实现其中三个方法:map() setup() cleanup ()
Partitioner分区
有默认实现HashPartitioner,逻辑是根据key的哈希值和numReduces来返回一个分区号;
1
| key.hashCode()&Integer.MAXVALUE % numReduces
|
如果业务上有特别的需求,可以自定义分区。
Comparable排序
- 当我们用自定义的对象作为key来输出时,就必须要实现WritableComparable接口,重写其中的compareTo()方法。
- 部分排序:对最终输出的每一个文件进行内部排序。
- 全排序:对所有数据进行排序,通常只有一个Reduce。
- 二次排序:排序的条件有两个。
Combiner合并
Combiner合并可以提高程序执行效率,减少IO传输。但是使用时必须不能影响原有的业务处理结果。
逻辑处理接口:Reducer
用户根据业务需求实现其中三个方法:reduce() setup() cleanup ()
- 默认实现类是
TextOutputFormat,功能逻辑是:将每一个KV对,向目标文本文件输出一行。
- 用户还可以自定义
OutputFormat。














